Fescue Toxicity
Tall fescue is a resilient forage source found in nearly 40 million acres of grazed pastures in the U.S. With nearly 17 million beef cows on tall fescue grasses annually, this common forage source also comes with a common issue: fescue toxicity.
Cattle consuming endophyte-infected tall fescue are negatively impacted by heat stress caused through constriction of the blood vessels. Numerous symptoms are displayed by cattle in efforts to cool themselves, none of which include cattle performing their best.
Introducing FesCool®
A Supplement Solution for Fescue Toxicity
Ask anyone who manages cattle on tall fescue and they’ll likely tell you about all the benefits that the forage provides their animals; fescue toxicity is just a risk that many producers have to deal with.
FesCool® is a new, low-moisture block formulated—and research proven—to help improve performance in cattle grazing endophyte-infected tall fescue.
Cattle fed FesCool® were able to improve blood circulation, a primary method of thermo-regulation, and increase feed intakes compared to the control groups.

Forage Intake *
In university research trials, growing cattle supplemented with FesCool® consuming a diet with high endophyte loads outperformed cattle without FesCool®, with or without endophyte loads.

- Forage intake was increased by 1.8 to 2.4 lbs per day. (P<0.001)
- ADG and feed efficiencies were improved. (P<0.001)
* Kansas State University Research
Physiological Response *
FesCool® improves the animals ability to cool itself through vasodilation of the blood vessels. The improvements in blood flow allow the animal to better regulate core body temperature through improved bloodflow to the extremities.
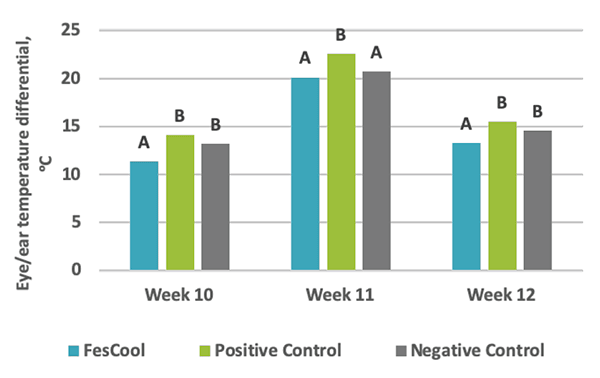
- Increase in coccygeal vein diameter by 17% compared to unsupplemented. (P<0.0.5)
- Increase in heat dissipation through extremities evidenced by 4.4°F (P<0.05) improvement in temperature differential.
* Kansas State University Research
Feeding Directions
Provide free-choice as a supplement to cattle at a rate of one block for each 15 to 25 head. Place blocks in pen or pasture near areas frequented by cattle, such as watering locations, shade or loafing areas. Cattle normally consume approximately 3/4 pound per head daily. Consumption may vary depending on climate, grazing conditions, condition of livestock and/or availablity of other feeds. In situations where climate and/or other factors result in consumption of less than 3/4 pound per head daily, intake of supplement can be increased slightly by providing additional blocks in each pen or pasture.
Provide access to fresh water and free-choice salt at all times.
CAUTION: Use as directed. Observe livestock and monitor intake daily.
Guaranteed Analysis
| CRUDE PROTEIN, MINIMUM | 36.0%* | COBALT, MINIMUM | 3 ppm |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRUDE FAT, MINIMUM | 5.0% | COPPER, MINIMUM | 300 ppm |
| CRUDE FIBER, MAXIMUM | 2.0% | IODINE, MINIMUM | 15 ppm |
| ADF, MAXIMUM | 1.5% | MANGANESE, MINIMUM | 1,200 ppm |
| CALCIUM, MINIMUM | 1.3% | SELENIUM, MINIMUM | 6.6 ppm |
| CALCIUM, MAXIMUM | 1.8% | ZINC, MINIMUM | 1,200 ppm |
| PHOSPHORUS, MINIMUM | 1.0% | VITAMIN A, MINIMUM | 80,000 IU/lb |
| MAGNESIUM, MINIMUM | 1.0% | VITAMIN D, MINIMUM | 8,000 IU/lb |
| POTASSIUM, MINIMUM | 3.0% | VITAMIN E, MINIMUM | 80 IU/lb |
* This includes not more than 18% equivalent crude protein as non-protein nitrogen.